How to Treat Brain Aneurysms With Babies Ai Dupont or Childrens Hospital in Philly
What is a cerebral aneurysm?
An aneurysm is a ballooned, weak surface area in the wall of an artery (blood vessel) supplying the encephalon. Brain aneurysms in children may be different to brain aneurysms in adults. Typically, aneurysms in children have no symptoms until they burst (rupture). A ruptured cerebral aneurysm tin can cause haemorrhage into the space around the brain, this is chosen a subarachnoid bleeding. This can extend within the brain and crusade a blockage of the normal fluid in the brain or put pressure on the brain.
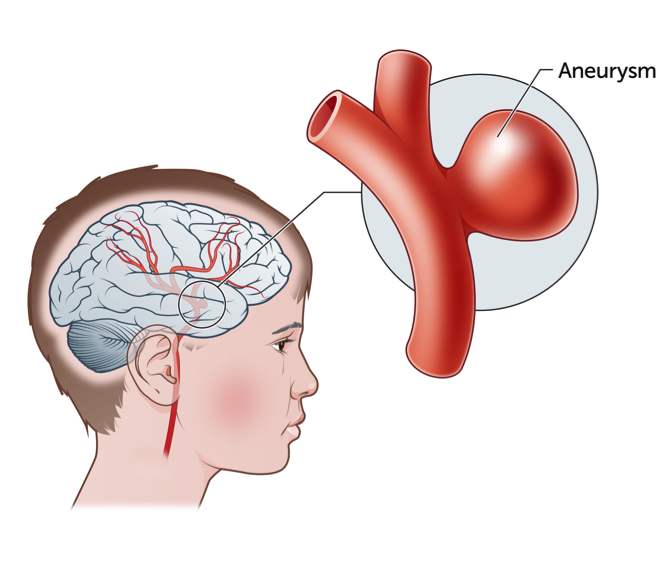
Signs and symptoms of a cerebral aneurysm
Unfortunately, the majority of patients with cerebral aneurysms don't know they have ane because the aneurysm typically causes no symptoms, until it bursts. A ruptured cerebral aneurysm will bleed over the surface of the brain and may extend into the brain, causing a haemorrhagic stroke.
What causes a cognitive aneurysm?
As children do not usually have any risk factors (such every bit high blood pressure, long-term excessive alcohol intake or high cholesterol) that increase their take chances of cognitive aneurysms, oftentimes the cause in children is not understood. Researchers are working to learn more about the potential causes of aneurysms in children such every bit whether at that place are any genetic changes that may make this more likely.
How are cerebral aneurysms diagnosed?
A cognitive aneurysm may exist diagnosed by a CT browse, or an MRI or MRA scan.
MRI/MRA scan: An MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) machine or scanner uses a powerful magnet to take very articulate and detailed pictures of the torso. It is useful for looking at many parts of the body and often gives actress information to apparently X-rays, ultrasounds or CT scans. During an MRI scan, the role of the trunk beingness scanned will have images taken from several different angles. There is no ionizing radiation (e.1000. 10-rays) used in an MRI and the magnetic field used in MRI is safe even during the second half of pregnancy.
In add-on to the MRI, an MRA may also be completed. An MRA or magnetic resonance angiogram specifically looks at the blood vessels in the brain and neck and those around the stroke. The MRA and MRI are completed at the same time during the same browse.
CT scan: a CT scan or computed tomography imaging is a type of X-ray. A CT scan is not painful. The CT scanner is a big open doughnut-shaped machine. Your kid will prevarication down on a tabular array, which moves through the centre of the machine at least twice during the scan. The CT scanner takes all of its pictures as the table is moving.
Your child will need to remain very even so for the pictures and sometimes concord their breath; normally this is for less than ten seconds. More often than not, the CT scan study takes virtually x–15 minutes in full. With and injection of CT dissimilarity (dye) a CT angiogram may be performed to evidence the blood vessels.
Cognitive angiogram: is an x-ray test where a dye (dissimilarity) is injected directly into an artery through the groin whilst your kid is under anaesthetic. This test gives detailed pictures of the arteries and veins (blood vessels) of the encephalon. This test is performed to look for abnormalities in blood vessels. Once the angiogram is completed, your child will be required to remain lying flat for four hours to ensure there is no bleeding from the artery in the groin.
All of these tests provide unlike information and your kid may need a combination of these to plan the optimal treatment for them.
Handling for Cerebral Aneurysms
A burst or ruptured aneurysm may require emergency surgery to drain cerebro-spinal fluid (CSF) (CSF is a articulate and colourless fluids that is found in the brain and spinal cord) from your kid's brain, to relieve pressure. A drain, known as an External Ventricular Device (EVD), may exist required, and drains CSF from the fluid pathways in the brain to an external collection bag.
One time an aneurysm has bled, the aneurysm needs urgent treatment to stop it from haemorrhage once again. At that place are two principal treatments for aneurysms. 1 treatment involves a surgical operation, and the other involves blocking the aneurysm through the blood vessels. The shape and location of each aneurysm determines which technique is the best choice to treat them. The treating squad caring for your kid will hash out these options and explain what is recommended for your child.
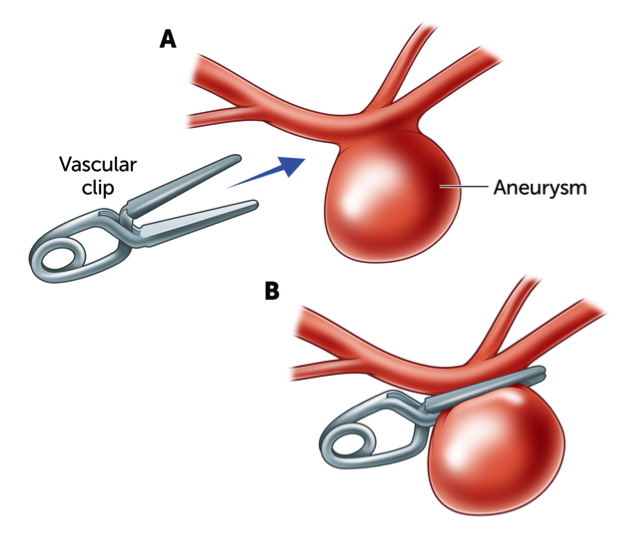
The surgical operation is referred to as 'clipping' an aneurysm which involves placing a titanium clip across the neck of the aneurysm, to stop blood flow into the aneurysm. Clipping of an aneurysm is performed under general anaesthetic. A modest opening is made in the skull by a neurosurgeon, this is called a craniotomy. Through the small opening, the brain is retracted (moved back) and the aneurysm is located. The small prune is then placed across the base, or the neck of the aneurysm to block the blood catamenia from inbound the aneurysm whilst allowing normal blood flow to continue in the main avenue. The clips are made from titanium and remain on the avenue forever.
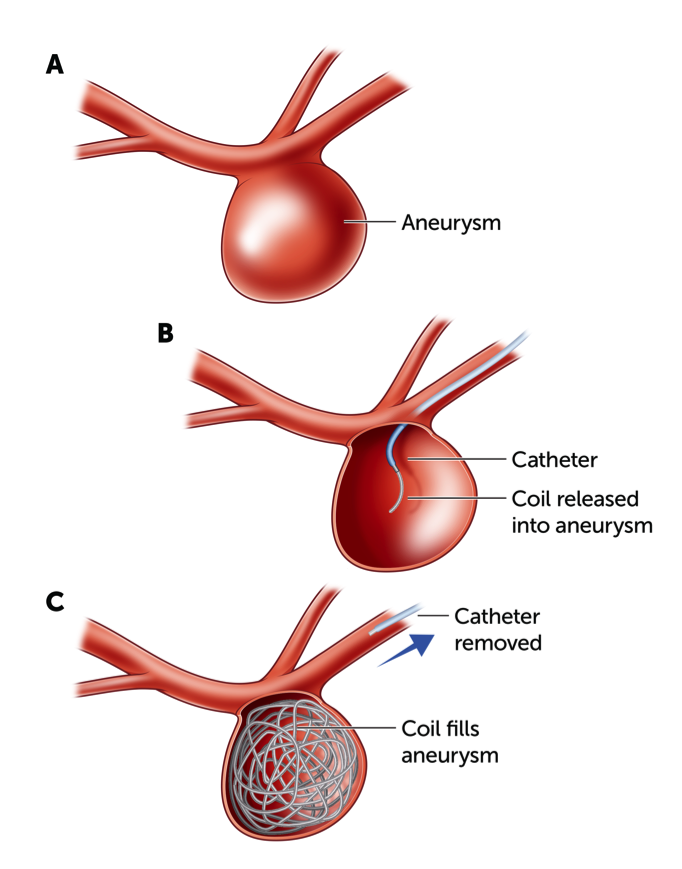
The other method of treatment is "coiling" an aneurysm. This involves filling the aneurysm with tiny platinum coils that crusade the blood inside the aneurysm to clot. Coiling is performed with tiny instruments (a catheter) that are guided along the claret vessels from an avenue in the groin. Complex aneurysms may besides exist managed by the placement of a stent. A stent is a tiny tube that is inserted into a blocked passageway to recreate a normal claret vessel channel. A stent stops the opening to the aneurysm.
Recovery post-obit clipping of a cerebral aneurysm
If the aneurysm has not burst, the average stay in infirmary is five days, with the overall recovery time typically taking four to six weeks. During this time, children will have restrictions on certain activities, such equally contact sports. Your child's md volition suggest on a gradual return to activities such as school, and sports following the surgery.
Recovery following coiling of a cerebral aneurysm
Immediately after the process is complete, your child needs to lay apartment for approximately half-dozen hours to avoid bleeding in the groin where the catheter was inserted. Patients are and then able to move effectually the room later on a few hours of strict bed rest. Coiling of aneurysms does non require open surgery to the brain, and therefore if the aneurysm has not burst recovery is quicker. Your kid'southward md will advise on a gradual render to activities such every bit school, and sports following the surgery.
After an aneurysm has ruptured
It is of import to understand that after an aneurysm has ruptured your child will need to recover from the bleed likewise equally having treatment of the aneurysm which prevents further bleeds.
As a result of the bleed, your child may experience problems with:
Vasospasm: a constriction or narrowing of the blood vessels in response to the bleed.
Hydrocephalus: a build-upward of the cerebro-spinal fluid (CSF) within the brain
Ischaemic Stroke: which may occur every bit a result of vasospasm or due to the build-up of pressure on the brain, obstructing the flow of blood.
Your kid'due south treating medical team will be watching for symptoms such equally:
- Altered level of consciousness
- weakness on one side of the face and/or body
- difficulty speaking
- confusion
- neck stiffness (less common)
- fever (less common)
In social club to closely monitor your child's progress following the bleed, your kid might need to take farther scans.
Follow-upwards
Your child should have regular surveillance imaging and follow-upwardly appointments with the Neurosurgery department at their infirmary.
Key points to recollect
- An aneurysm is a ballooned, weak area in the wall of an artery (blood vessel) supplying the encephalon.
- Aneurysms in children take no symptoms until they burst (rupture) causing haemorrhage into the space around the brain.
- Cerebral aneurysms tin be diagnosed on a CT scan, MRI or cerebral angiogram.
- Treatment for cerebral aneurysms include clipping or coiling of the aneurysm.
- Recovery following the rupture of an aneurysm tin take many weeks.
For more than information
- Haemorrhagic Stroke Kids Wellness Info Fact Canvass
- https://strokefoundation.org.au/
- https://brainfoundation.org.au/
Common questions our doctors are asked
When can my child render to schoolhouse?
The elapsing that each kid takes to recover from treatment for a cerebral aneurysm varies for each individual and is dependent upon what form of treatment was required and whether the aneurysm was un-ruptured or had bled. If your child suffered an intracranial bleed, their recovery may be much longer and they may not be able to return to school for several months and they may require a period of outpatient rehabilitation. Render to schoolhouse may be possible sooner if your child has had treatment for an un-ruptured aneurysm.
Can my kid resume normal sporting activities after clipping or coiling of a cognitive aneurysm?
Normal sporting activities can be resumed later on clipping or coiling of a cerebral aneurysm simply this should only be resumed after consultation with your treating doctor, and is likely to exist following several weeks of recovery. Sports should be introduced gradually, with not-contact sports permitted first and contact sports only later total recovery including adequate healing of a craniotomy site (ordinarily three months).
Can my child have an MRI or go through metal detectors subsequently clipping or coiling of an aneurysm?
All of the mod clips, coils and stents are prophylactic for clinical MRI ( non high strength scans) and will not activate metal detectors. However all patients undergoing an MRI scan must complete a safety questionnaire to decide if they have whatsoever implants. This must be completed every bit not all patients with implants can accept an MRI browse. Each implant has a unique reference and provided this information is available prior to your appointment. The MRI team can determine whether an MRI scan is prophylactic for your child. If the information is not available, the decision to make up one's mind if your child tin can safely accept a scan is complex and may pb to the browse being cancelled so information technology's very important that you bring any information you have virtually the implant to your appointment. Some implants may be able to be scanned on a i.v T rather than a stronger 3T magnet. Metallic artefact volition be created in the area effectually the implants, which may obscure some anatomical detail.
The coils used to treat a patient's vascular malformation will be documented in the patient record and will demand to be checked to ensure MRI safety. Aneurysm clips and endovascular coils will not be detected when your kid walks through a metal detector but may be detected by loftier strength hand held devices.
Developed by The Majestic Children's Hospital Neurology and Neurosurgery departments. We admit the input of RCH consumers and carers.
Reviewed April 2020
Kids Health Info is supported by The Regal Children'due south Infirmary Foundation. To donate, visit www.rchfoundation.org.au.
Source: https://www.rch.org.au/kidsinfo/fact_sheets/Cerebral_Aneurysm/
Enregistrer un commentaire for "How to Treat Brain Aneurysms With Babies Ai Dupont or Childrens Hospital in Philly"